The role of Federal Reserve in the US Financial System
The Federal Reserve System is the central banking system of the United States. The Federal Reserve System is composed of several layers. It is governed by the presidentially-appointed board of governance or Federal Reserve Board. In response to the financial panic of 1907 The Fed was established by the President Woodrow Wilson on 23 Dec. 1913.
Before that the U.S. was the only major financial power without a central bank. Its creation was precipitated by repeated financial panics that afflicted the U.S. economy over the previous century, leading to severe economic disruptions due to bank failures and business bankruptcies. A crisis in 1907 led to calls for an institution that would prevent panics and disruptions.
The New York Fed works within the Federal Reserve System to foster economic and financial stability and vitality throughout the Second District and the United States. Banks are also needed support to keep credit flowing. When financial markets are clogged, firms tend to draw on bank lines of credit, which can lead banks to pull back on lending or selling Treasury and other securities.
The role of Federal Reserve in the US financial system
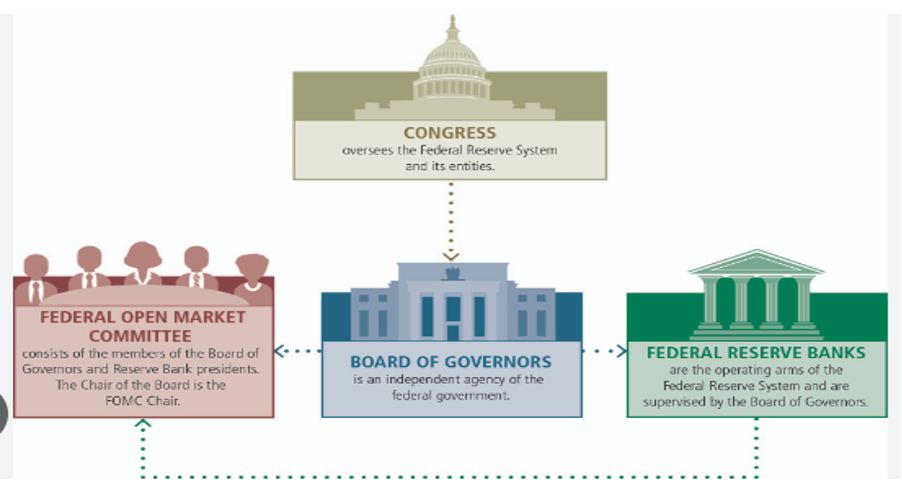
The Federal Reserve is the most important part of the US financial system. It is responsible for regulating the banks and ensuring the stability of the financial system. It also plays a role in monetary policy, which is the government’s strategy for controlling inflation and unemployment.
The Federal Reserve is responsible for the stability of the United States financial system. By monitoring internal and external influences, and preventing any future crisis, the Federal Reserve is able to safeguard the economy as a whole. Additionally, the Federal Reserve supervises the activities of financial institutions and controls their impact on the economy.
Finally, the Federal Reserve works to ensure a glitch-free, secure system for payment gateways. The Federal Reserve strives to achieve three major objectives through its monetary policy – maximum employment, stable prices, and low long-term interest rates. By controlling the availability
of credit in the economy, the Federal Reserve can influence inflation, investment, and other economic parameters.
The Federal Reserve also ensures the stability of the US financial system, monitoring internal and external threats. By doing so, the Federal Reserve
protects the economy from potential shocks that could destabilize it. The Federal Reserve has several tools it can use to pursue its monetary policy objectives. These tools include open market operations, the discount rate, and reserve requirements.
Open market operations involve the purchase and sale of government securities. When the Federal Reserve buys government securities, it increases the money supply and lowers interest rates. When the Federal Reserve sells government securities, it decreases the money supply and raises interest rates.
The discount rate is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve charges banks for short-term loans. The Federal Reserve can change the discount rate to influence the overall level of borrowing in the economy.
Reserve requirements are the percentage of deposits that banks must hold as reserves at the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve can change reserve requirements to either encourage or discourage lending.
Impact on stock trading
Fed’s decisions about interest rates can affect how much money is available for investors to borrow. When the Fed reduces interest rates, it makes it cheaper for investors to borrow money, which can lead to more investment in stocks. Additionally, the Fed can also use its power to change the supply of money to try to influence the stock market. For example, if the Fed wants to increase the amount of money in the economy, it can buy government bonds, which will increase the amount of money in the system. This can lead to a higher stock market because there is more money available to invest and vice versa.
There is evidence that the Fed does have an impact on stock prices. One study found that a one-percentage-point increase in the federal funds rate leads to a 0.5-percentage-point decrease in the S&P 500 Index. Another study found that a one-dollar increase in the money supply leads to a 0.75-dollar increase in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
While there is evidence that the Fed has an impact
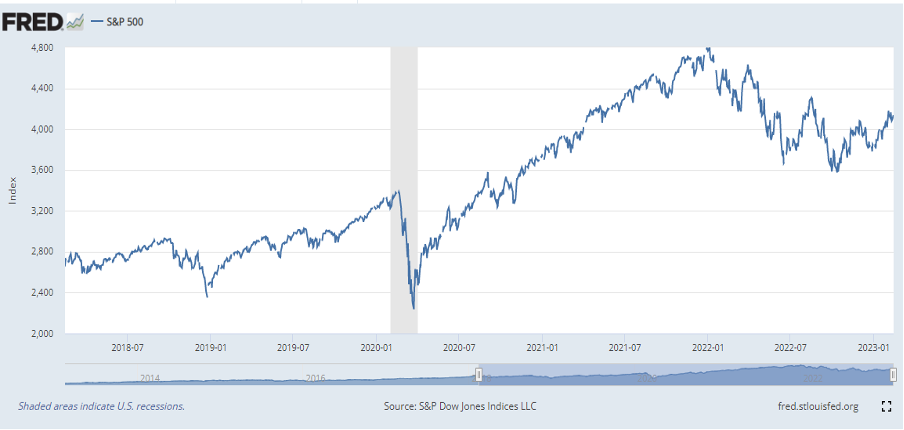
The chart shows that when the Fed enters a rate-rising cycle, the economy grows faster and the stock market can yield higher returns than the bond market.
The S&P 500 is regarded as a gauge of the large cap U.S. equities market. The index includes 500 leading companies in leading industries of the U.S. economy, which are publicly held on either the NYSE or NASDAQ, and covers 75% of U.S. equities. Since this is a price index and not a total return index, the S&P 500 index here does not contain dividends.
Conclusion
To sum up, the Federal Reserve plays a major role in the US financial system, and it has a significant influence on stock trading. By keeping inflation, interest rates, and investment activity within a manageable range, the Federal Reserve provides stability to the market and preserves investor confidence.
Understanding the role of the Federal Reserve and its broad impact on stock trading is essential for investors. With the insight gained from this post, investors can make better informed decisions and protect their investments from the turbulence of the markets. As the Federal Reserve takes a proactive role in the US financial system, investors must stay informed of its actions and adjust their strategies accordingly.







